Introduction of Meteorological Services (MET)
I. General
Most of flight activities take place in the atmosphere, since aviation and meteorology have a close and inseparable connection. This connection is expressed in two aspects. First, the aircraft can not be able to fly without the reflection force of the atmosphere. In contrast, sometime atmospheric phenomena make negative impacts on flight activities.
According to the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) statistics, conditioned weather is responsible for about 70% of delayed flights. Moreover, weather plays an important role in causing incidents and aviation accidents. In addition, the bad weather is also causing major economic losses for the airline industry. In Vietnam, according to the statistics of the Division of Safety and Security, Vietnam Air Management Corporation, the number of flight operations is affected by the weather (delay flight, waiting flight, flying round off the FIR boundary, missing landing, returning flight, or destination alternate aerodromes) accounts for 50-60% of the total number of incidents in the annual safety report of the Corporation. Having said that, this number does not include the number of canceled flights due to the airport closure in particularly bad weather such as storms or floods or bad weather (CB, noise, freezing) on the flight that does not enter the FIR / national border. Therefore, weather information, weather forecasts and warnings are an indispensable part of the civil aviation industry in every country.
In order to ensure the meteorological service for air navigation, the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has issued the Meteorological Service for International Air Navigation, Standards and recommendations apply to civil aviation meteorological work for all member states. Accordingly, each country's aviation meteorological service is responsible for providing data, products (monitoring, forecasting and warning) to users in accordance with regulations to ensure safety, And the effectiveness of domestic and international aviation. In addition, aviation meteorological services contribute to the reduction of aircraft emissions and global climate change impacts, while also enhancing the ability to control and exploit the skies in the notification areas. Flying (FIRs). On the other hand, aeronautical meteorological services also serve for in emergency and aviation search and rescue, aeronautical information service and investment research for the construction of aerodromes (airports), the opening of new routes.
II. Organizational Structure of Viet Nam Aeronautical Meteorological Services
According to the Vietnam Civil Aviation Law, Aeronautical Meteorological Services is one of five Civil Air Navigation Services, including: ATS (Air Traffic Services); CNS (Communication, Navigation and Surveillance Services); AIS (Aeronautical Information Services); MET (Aeronautical Meteorological Services); SAR (Search and Rescue Service). MET services must be provided 24 hours a day, ensuring accuracy, continuity, timeliness and completeness for each stage in the closed cycle operation of a flight (flight planning, Pre-flight briefings, flight stages, etc.). Currently, the MET Services in Vietnam is under the responsibility of VATM (Vietnam Air Traffic Management Corporation) with a system of aerodrome meteorological offices including:
- Meteorological Watch Centre, whose main function is to manage and organize the activities related to maintain continuous watch over meteorological conditions affecting flight operations; prepare and issue SIGMET; supply weather advisory information in order to serve flight operation over flight routes, within Vietnam air spaces and Flight Information Regions over international maritime under the management of Vietnam.
- Aerodrome Meteorological Centers, including Noi Bai, Da Nang and Tan Son Nhat Aerodrome Meteorological Centre, belongs to the Northern, Middle and Southern Region Air Traffic Services Company, respectively, whose main function is to manage and organize the activities related to weather observation, forecasting and warning at airports serving aircraft for landing and take-off operations, and provide briefings, consultation and supply meteorological flight documentation to flight crew members, airlines and other users within its area of responsibility.
- 22 Aeronautical Meteorological Stations at international airports and domestic airports are under the responsibility of the Northern, Middle and Southern Region Air Traffic Services Company, respectively, whose main function is observe and prepare METAR, SPECI and landing forecasts (TREND) serving aircraft for landing and take-off operations.
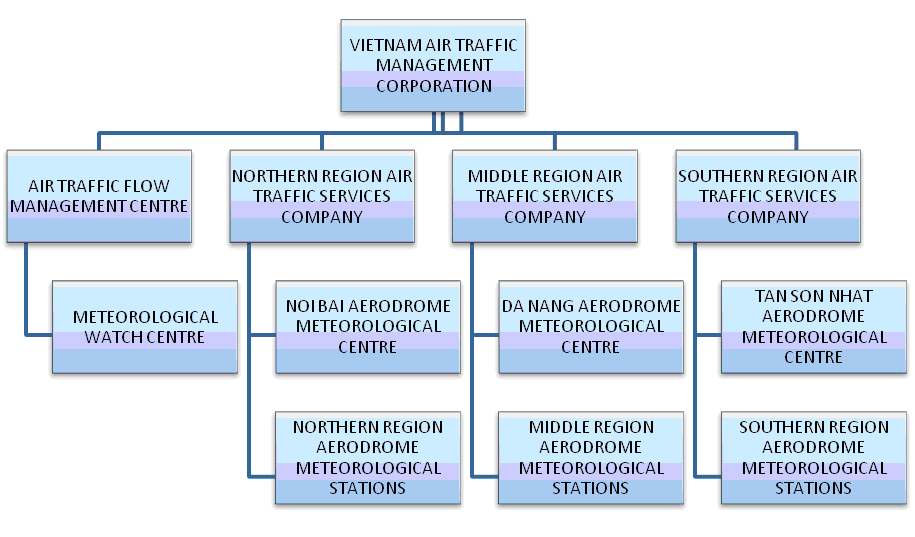
Organizational Chart Aerospace Service Systems
III. Products
The objective of meteorological service for international air navigation shall be to contribute towards the safety, regularity and efficiency of international air navigation. To accomplish the above goals successfully, the aviation meteorological services collect process and produce products for users according to ICAO recommended standards.
1. Aerodromes weather observations report
Aerodromes weather observations shall be made by facilities, tools, and visual calculations. Aerodromes weather reports serve for flight planning, arriving and departing aircraft, en-route flight and other aeronautical operational activities. In addition, the Aerodromes weather observation data is one of the data used for aerodrome weather forecast.
Aerodromes routine reports are being make every 30 minute. In case of significant changes happen beyond criteria, special weather report will be issued in order to ensure that users are updated with aerodromes weather information.
2. Forecasts, warnings
The aeronautical Meteorological Office provide weather forecasting/warning services for civil aviation activities on their areas of responsibility. Forecasting and warning messages include:
- Aerodrome forecast (TAF, TAF AMD).
- Landing forecast.
- Takeoff forecast.
- Area and air route forecast.
- SIGMET.
- AIRMET.
- Aerodrome warning (AD WRNG).
- Windshear warning (WS WRNG).
2.1 Aerodrome forecasts
An aerodrome forecast shall be issued at a specified time and consist of a concise statement of the expected meteorological conditions at an aerodrome for a specified period.
Meteorological offices preparing TAF shall keep the forecasts under continuous review and, when necessary, shall issue amendments promptly to to ensure that users are always using the updates.
2.2. Landing forecasts
A landing forecast shall consist of a concise statement of the expected significant changes in the meteorological conditions at that aerodrome to be appended to a local routine report, local special report, METAR or SPECI. The period of validity of a trend forecast shall be 2 hours from the time of the report which forms part of the landing forecast.
2.3 Forecasts for take-off
A forecast for take-off should refer to a specified period of time and should contain information on expected conditions over the runway complex in regard to surface wind direction and speed and any variations thereof, temperature, pressure (QNH), and any other elements as agreed locally. They are used for serving aircraft during take-off.
2.4 En-route weather forecasts
Weather conditions forecasts on the flight and flight regions, including additional forecasts, including information on upper winds, temperatures, hazadous weather phenomena, convective clouds…
2.5. SIGMET Information
SIGMET information shall be issued by a meteorological watch office and shall give a concise description in abbreviated plain language concerning the occurrence or expected occurrence of specified en-route weather and other phenomena in the atmosphere that may affect the safety of aircraft operations, and of the development of those phenomena in time and space. In addition, SIGMET is also used for flight planning.
2.6. AIRMET Information
AIRMET information shall be issued by a meteorological watch office in accordance with regional air navigation agreement, taking into account the density of air traffic operating below flight level 100. AIRMET information shall give a concise description in abbreviated plain language concerning the occurrence and/or expected occurrence of specified en-route weather phenomena. which may affect the safety of low-level flights, and of the development of those phenomena in time and space Currently, AIRMET not been implemented in Vietnam. However, this information will be made in the future to accommodate the growth of flying activity, especially low-level flight.
2.7 Aerodrome warnings
Aerodrome warnings shall be issued by the aerodrome meteorological offices and shall give concise information of meteorological conditions which could adversely affect aircraft on the ground, including parked aircraft, and the aerodrome facilities and services.
2.8 Wind shear warnings and alerts
Wind shear warnings shall be prepared by the aerodrome meteorological offices designated by the meteorological authority concerned for aerodromes where wind shear is considered a factor, in accordance with local arrangements with the appropriate ATS unit and operators concerned. Wind shear warnings shall give concise information on the observed or expected existence of wind shear which could adversely affect aircraft on the approach path or take-off path or during circling approach between runway level and 500 m (1 600 ft) above that level and aircraft on the runway during the landing roll or take-off run. Where local topography has been shown to produce significant wind shears at heights in excess of 500 m.
3. Other products
3.1 Flight document and briefing, consulting
At airports, flight crews or operators, are provided with a meteorological document that includes presentations and advice on weather information. Meteorological documents are meteorological information presented in maps, tables and text form for the crew to use during the flight. Presentations and consultations are conducted by direct dialogue or by other means of communication between the meteorological staff and the users.
At the Hanoi ACC, there is a meteorological unit to provide live presentations and consultations to Air Traffic Controllers for flight control operations. In the near future, the VATM will research to expand the model at Ho Chi Minh ACC as well as other Air trafic control units to contribute towards the safety,regularity and efficiency of international air navigation
At airports, airports, flight crews or flight attendants, the flight crew is provided with a meteorological record that includes presentations and advice on weather information. Meteorological records are meteorological information presented in maps, tables and newsletters for the crew to use during the flight. Lectures and consultations are conducted by direct dialogue or by other means of communication between the meteorological staff and the users.

Meteorological unit at Ha Noi ACC
3.2 Aeronautical climatological information
Aeronautical aviation data is mainly provided to to aeronautical users for flight planning, especially new route planning.
.png)
An example of a SIGMET in graphical form
IV. Conclusion
Vietnam is one of the countries in the region with the strongest growth in aviation. Meanwhile, Vietnam is also a country with severe weather and climate. As a result, aviation meteorological services have been invested and developed by the authorities to better serve the aviation industry, contributing to the country's economy.
Aeronautical meteorological services play an important role in ensuring that airfares operate safely and efficiently. Aeronautical meteorological information should be provided on a continuous, timely, adequate and reliable basis for each stage of the closed loop operation of the flight. The development process of the aviation industry in general, civil aviation in Vietnam in particular, requires the aviation meteorological service providers to continuously update and improve production lines as well as human resource to keep pace with consumer demand; especially emphasize the application of advanced technologies to not only improve the quality of meteorological products but also raise the efficiency of exploitation of products for and management and services, and finally integrate with the development of aerospace industry in the region and the world.




















